Expo
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Clinical Chem.Molecular DiagnosticsHematologyImmunologyMicrobiologyPathologyTechnologyIndustry
Events

- POC Biomedical Test Spins Water Droplet Using Sound Waves for Cancer Detection
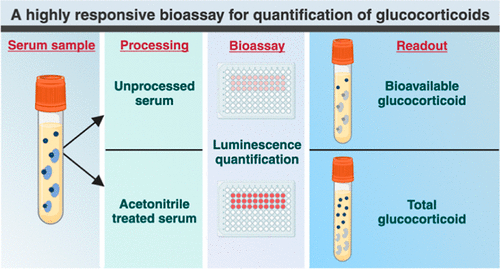
- Highly Reliable Cell-Based Assay Enables Accurate Diagnosis of Endocrine Diseases
- New Blood Testing Method Detects Potent Opioids in Under Three Minutes
- Wireless Hepatitis B Test Kit Completes Screening and Data Collection in One Step
- Pain-Free, Low-Cost, Sensitive, Radiation-Free Device Detects Breast Cancer in Urine
- Blood Test Could Detect HPV-Associated Cancers 10 Years before Clinical Diagnosis
- Low-Cost Point-Of-Care Diagnostic to Expand Access to STI Testing
- 18-Gene Urine Test for Prostate Cancer to Help Avoid Unnecessary Biopsies
- Urine-Based Test Detects Head and Neck Cancer
- Blood-Based Test Detects and Monitors Aggressive Small Cell Lung Cancer
- First 4-in-1 Nucleic Acid Test for Arbovirus Screening to Reduce Risk of Transfusion-Transmitted Infections
- POC Finger-Prick Blood Test Determines Risk of Neutropenic Sepsis in Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
- First Affordable and Rapid Test for Beta Thalassemia Demonstrates 99% Diagnostic Accuracy
- Handheld White Blood Cell Tracker to Enable Rapid Testing For Infections
- Smart Palm-size Optofluidic Hematology Analyzer Enables POCT of Patients’ Blood Cells
- AI Tool Precisely Matches Cancer Drugs to Patients Using Information from Each Tumor Cell
- Genetic Testing Combined With Personalized Drug Screening On Tumor Samples to Revolutionize Cancer Treatment
- Testing Method Could Help More Patients Receive Right Cancer Treatment
- Groundbreaking Test Monitors Radiation Therapy Toxicity in Cancer Patients
- State-Of-The Art Techniques to Investigate Immune Response in Deadly Strep A Infections
- Unique Metabolic Signature Could Enable Sepsis Diagnosis within One Hour of Blood Collection
- Simple Blood Test Combined With Personalized Risk Model Improves Sepsis Diagnosis
- Groundbreaking Diagnostic Platform Provides AST Results With Unprecedented Speed
- Blood Analysis Predicts Sepsis and Organ Failure in Children
- TB Blood Test Could Detect Millions of Silent Spreaders
- DNA Biosensor Enables Early Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
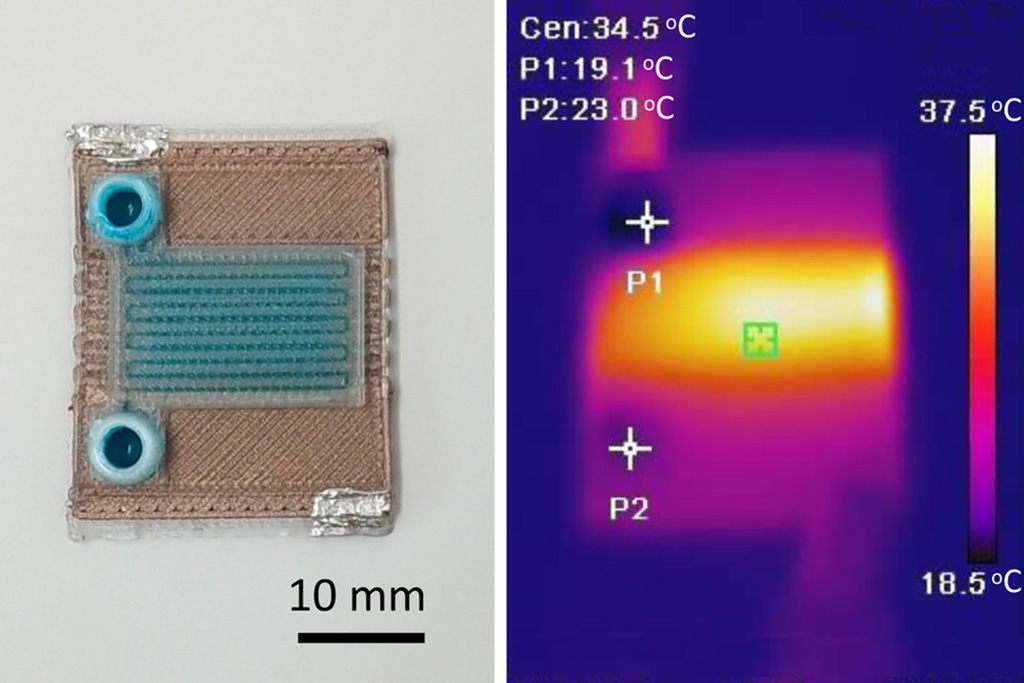
- Self-Heating Microfluidic Devices Can Detect Diseases in Tiny Blood or Fluid Samples
- Breakthrough in Diagnostic Technology Could Make On-The-Spot Testing Widely Accessible
- First of Its Kind Technology Detects Glucose in Human Saliva
- Electrochemical Device Identifies People at Higher Risk for Osteoporosis Using Single Blood Drop
- Bosch and Randox Partner to Make Strategic Investment in Vivalytic Analysis Platform
- Siemens to Close Fast Track Diagnostics Business
- Beckman Coulter and Fujirebio Expand Partnership on Neurodegenerative Disease Diagnostics
- Sysmex and Hitachi Collaborate on Development of New Genetic Testing Systems
- Sysmex and CellaVision Expand Collaboration to Advance Hematology Solutions
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- Unique Hand-Warming Technology Supports High-Quality Fingertip Blood Sample Collection
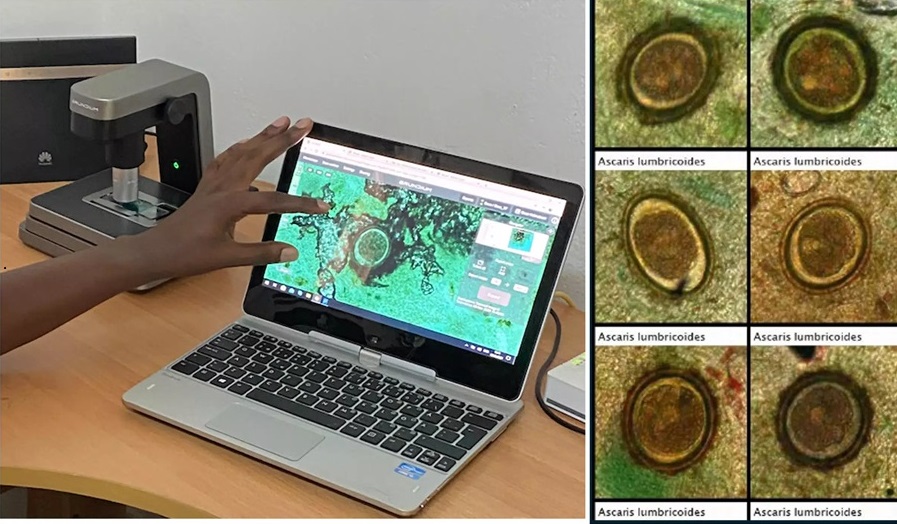
- Image-Based AI Shows Promise for Parasite Detection in Digitized Stool Samples
- Deep Learning Powered AI Algorithms Improve Skin Cancer Diagnostic Accuracy
- Microfluidic Device for Cancer Detection Precisely Separates Tumor Entities
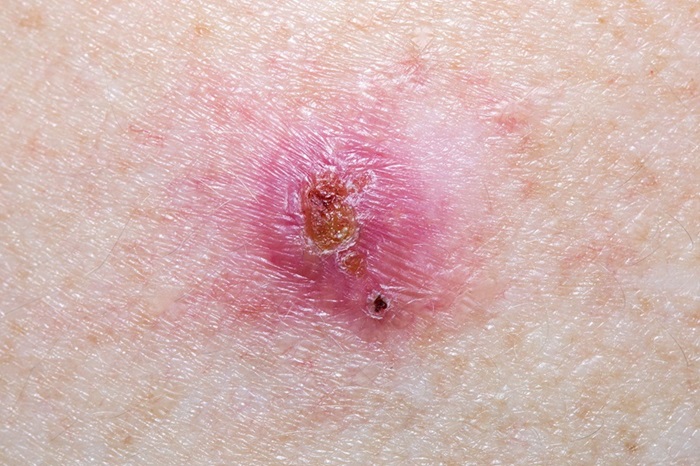
- Virtual Skin Biopsy Determines Presence of Cancerous Cells

Expo
 view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Clinical Chem.Molecular DiagnosticsHematologyImmunologyMicrobiologyPathologyTechnologyIndustry
Events
Advertise with Us
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
view channel
Clinical Chem.Molecular DiagnosticsHematologyImmunologyMicrobiologyPathologyTechnologyIndustry
Events
Advertise with Us


- POC Biomedical Test Spins Water Droplet Using Sound Waves for Cancer Detection
- Highly Reliable Cell-Based Assay Enables Accurate Diagnosis of Endocrine Diseases
- New Blood Testing Method Detects Potent Opioids in Under Three Minutes
- Wireless Hepatitis B Test Kit Completes Screening and Data Collection in One Step
- Pain-Free, Low-Cost, Sensitive, Radiation-Free Device Detects Breast Cancer in Urine
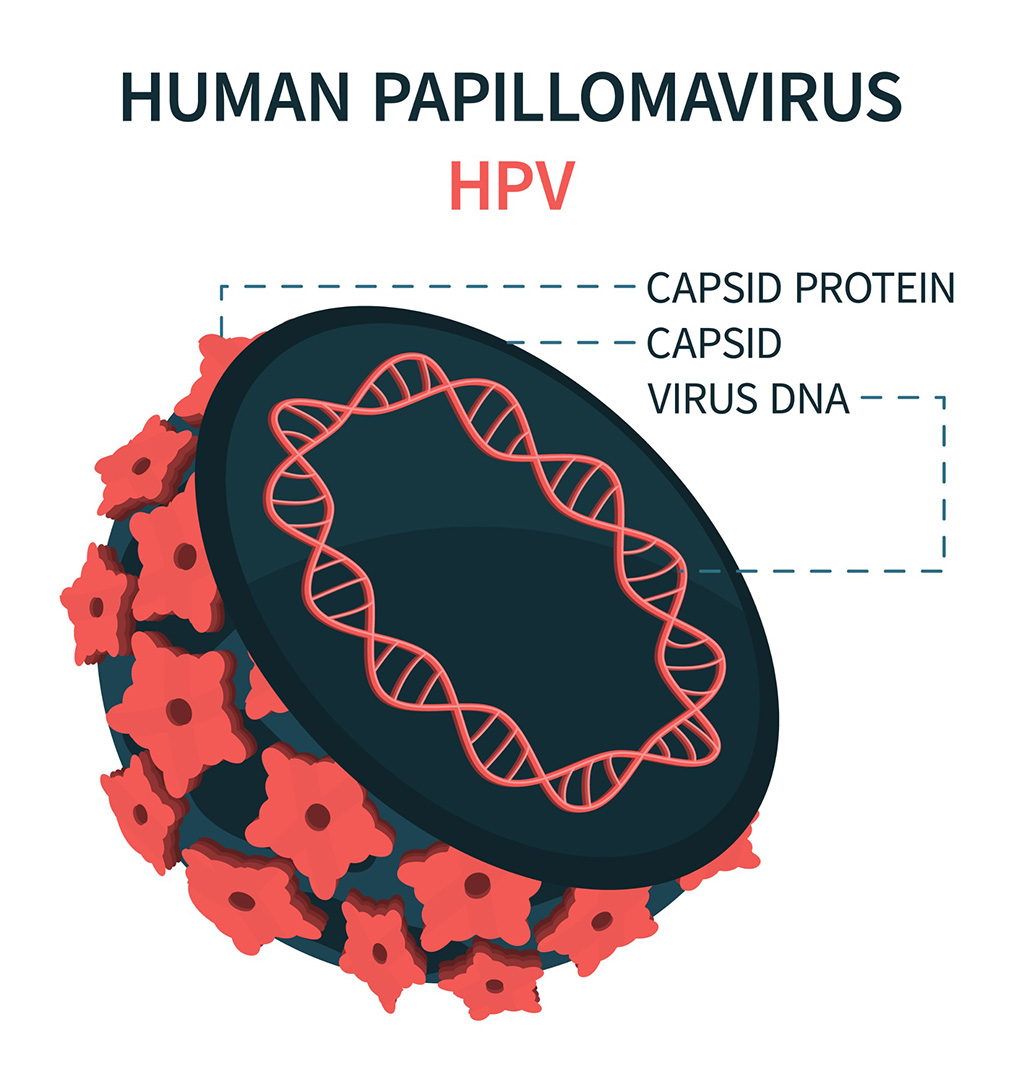
- Blood Test Could Detect HPV-Associated Cancers 10 Years before Clinical Diagnosis
- Low-Cost Point-Of-Care Diagnostic to Expand Access to STI Testing
- 18-Gene Urine Test for Prostate Cancer to Help Avoid Unnecessary Biopsies
- Urine-Based Test Detects Head and Neck Cancer
- Blood-Based Test Detects and Monitors Aggressive Small Cell Lung Cancer
- First 4-in-1 Nucleic Acid Test for Arbovirus Screening to Reduce Risk of Transfusion-Transmitted Infections
- POC Finger-Prick Blood Test Determines Risk of Neutropenic Sepsis in Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
- First Affordable and Rapid Test for Beta Thalassemia Demonstrates 99% Diagnostic Accuracy
- Handheld White Blood Cell Tracker to Enable Rapid Testing For Infections
- Smart Palm-size Optofluidic Hematology Analyzer Enables POCT of Patients’ Blood Cells
- AI Tool Precisely Matches Cancer Drugs to Patients Using Information from Each Tumor Cell
- Genetic Testing Combined With Personalized Drug Screening On Tumor Samples to Revolutionize Cancer Treatment
- Testing Method Could Help More Patients Receive Right Cancer Treatment
- Groundbreaking Test Monitors Radiation Therapy Toxicity in Cancer Patients
- State-Of-The Art Techniques to Investigate Immune Response in Deadly Strep A Infections
- Unique Metabolic Signature Could Enable Sepsis Diagnosis within One Hour of Blood Collection
- Simple Blood Test Combined With Personalized Risk Model Improves Sepsis Diagnosis
- Groundbreaking Diagnostic Platform Provides AST Results With Unprecedented Speed
- Blood Analysis Predicts Sepsis and Organ Failure in Children
- TB Blood Test Could Detect Millions of Silent Spreaders
- DNA Biosensor Enables Early Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
- Self-Heating Microfluidic Devices Can Detect Diseases in Tiny Blood or Fluid Samples
- Breakthrough in Diagnostic Technology Could Make On-The-Spot Testing Widely Accessible
- First of Its Kind Technology Detects Glucose in Human Saliva
- Electrochemical Device Identifies People at Higher Risk for Osteoporosis Using Single Blood Drop
- Bosch and Randox Partner to Make Strategic Investment in Vivalytic Analysis Platform
- Siemens to Close Fast Track Diagnostics Business
- Beckman Coulter and Fujirebio Expand Partnership on Neurodegenerative Disease Diagnostics
- Sysmex and Hitachi Collaborate on Development of New Genetic Testing Systems
- Sysmex and CellaVision Expand Collaboration to Advance Hematology Solutions
- Gene Panel Predicts Disease Progession for Patients with B-cell Lymphoma
- New Method Simplifies Preparation of Tumor Genomic DNA Libraries
- New Tool Developed for Diagnosis of Chronic HBV Infection
- Panel of Genetic Loci Accurately Predicts Risk of Developing Gout
- Disrupted TGFB Signaling Linked to Increased Cancer-Related Bacteria
- Unique Hand-Warming Technology Supports High-Quality Fingertip Blood Sample Collection
- Image-Based AI Shows Promise for Parasite Detection in Digitized Stool Samples
- Deep Learning Powered AI Algorithms Improve Skin Cancer Diagnostic Accuracy
- Microfluidic Device for Cancer Detection Precisely Separates Tumor Entities
- Virtual Skin Biopsy Determines Presence of Cancerous Cells


















.jpg)
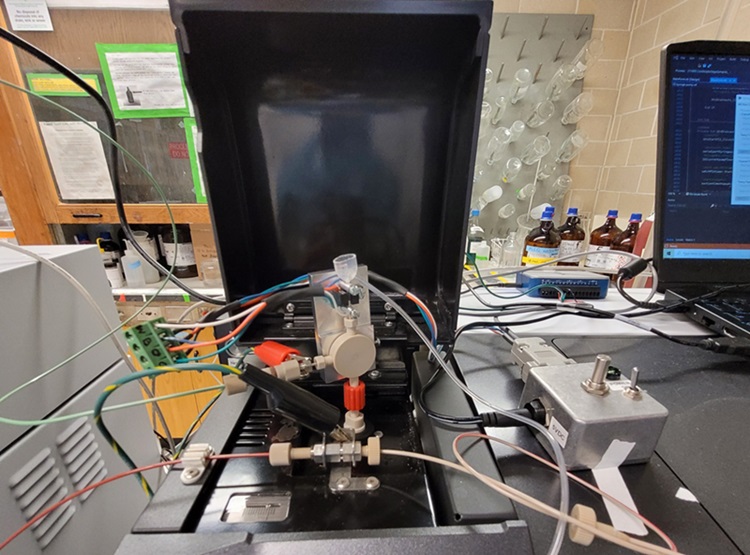







.jpg)

.jpg)